PMO Service Catalogue Addendum
With the House of PMO certification courses, there is extra content – an addendum – to the Service Catalogue which is utilised during the training courses.

Introduction
This addendum to the PMO Service Catalogue provides a wider context than just the development and maintenance of the service catalogue; it covers the setup, running and closing of the services themselves.
The addendum also includes additional services not found in the published version of the Service Catalogue.
Service Management within the PMO
1. DEFINITION OF A PMO SERVICE
One or more activities undertaken to produce an output for a customer that delivers a desired outcome for the organisation.
In order to deliver PMO services, a PMO must have:
- Individuals with the right level of competence
- Organisation/PMO governance and infrastructure
- Capacity
The setting up or closing down of a service can be run as a project and the Centre of Excellence may have standard processes, procedures, tools and templates.
2. SELECTION OF PMO SERVICES TO BE DELIVERED
PMOs deliver services where it is more effective, efficient or economically advantageous for them to do so than other people within the delivery organisation, or when control needs to be applied. The PMO may outsource all or part of the delivery of the service to others within or external to the organisation.
PMOs have many customers – all with their own needs and wants from the PMO. Any services to be delivered by a PMO will be aligned to the vision of the PMO(s) which in turn is aligned to the strategy of the organisation.
PMO governance ensures that the mix of PMO services provided are appropriately resourced and funded. The decision to setup a new PMO service is supported by information provided in a PMO Service Strategy, but cannot be taken in isolation of the other services currently being provided and those in setup. Due to limited capability, capacity, or funding, agreeing to setting up a new service, may require closing another.
3. PMO SERVICE ROLES
3.1. PMO Service Owner
A role undertaken within the PMO, accountable for the setup, running and closing of PMO services that deliver the required objectives. The role includes the monitoring of PMO service outcomes and KPIs and ensure any risks and issues are addressed.
This role is appointed by the PMO Director and is typically undertaken by a PMO Director or a PMO Manager.
3.2. PMO Service Manager
A role undertaken within the PMO, responsible for the day to day running of the PMO service. The role includes KPI reporting in relation to the PMO services.
This role is typically undertaken by a PMO Manager or a PMO Analyst.
3.3. PMO Service Operative
A role undertaken within the PMO and/or on behalf of the PMO, responsible for the execution of the process(es) required to deliver the outputs of the PMO service.
If the role is undertaken within the PMO, the role is typically undertaken by one or more PMO Analysts or PMO Administrators.
NB: The role of PMO Service Owner, PMO Service Manager and PMO Service Operative may all be held by one person. Where a PMO service is delivered by multiple PMOs, there may be multiple PMO Service Managers.
4. KEY DOCUMENTATION
4.1. PMO Service Strategy
The PMO service strategy is a key document that provides the PMO’s strategy for delivering services to its customers, including:
- How the requested services will be prioritised (typically based on alignment to the PMO vision and contribution to the strategy of the organisation)
- The principles for applying resources and funding for the services (including principles for recharging).
Ideally, there is a single PMO Service Strategy for the organisation – identifying how all the PMO services are provided via the various PMOs throughout the organisation.
The PMO Service Strategy is owned by the PMO Director.
4.2. PMO Service Catalogue
Details to be found in the core text.
4.3. PMO Operations Handbook
The PMO Operations Handbook details all the procedures that are undertaken within the PMO. They detail the RACI (who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed) for each constitute activity, along with the specific tools and techniques used. They cover all activities required to deliver and monitor the PMO Services along with activities required to undertake performance monitoring of the PMO.
For some organisations, the PMO Operations Handbook will also contain procedures required to recharge the services as determined in the PMO Service Strategy.
The PMO Operations Handbook is owned by the PMO Manager.
5. PMO SERVICE DELIVERY
5.1. Setting Up a PMO Service
Setting up a PMO Service includes the design, test/ pilot and transition of the PMO service into PMO operations.
When a decision has been made to commence delivery of a service, the PMO Director and PMO Manager(s) will agree which PMO(s) is best placed to deliver or manage the outsourcing of the service and, where appropriate, appoint relevant PMO Service Manager(s).
Considerations in this decision include:
- Content of the PMO Service Strategy
- Available competence and capacity
- Other services currently delivered by that PMO
- The customers and stakeholders
- The scope of the service (a project/ programme, multiple projects or programmes, portfolio or organisation)
In some situations, where there is a lack of internal competence to deliver the service, it may still be preferable to invest time and effort to develop the competence than outsource the service.
Using the content of the Service Strategy (and any useful artefacts from any current or previously delivered PMO service) the high level process(es) required to underpin PMO service are defined and agreed with the relevant stakeholder and contributors.
The process can be documented in a SIPOC table/ diagram (Suppliers/ Inputs/ Process/ Outputs/ Customer – see below) and forms part of the entry within the PMO Service Catalogue.
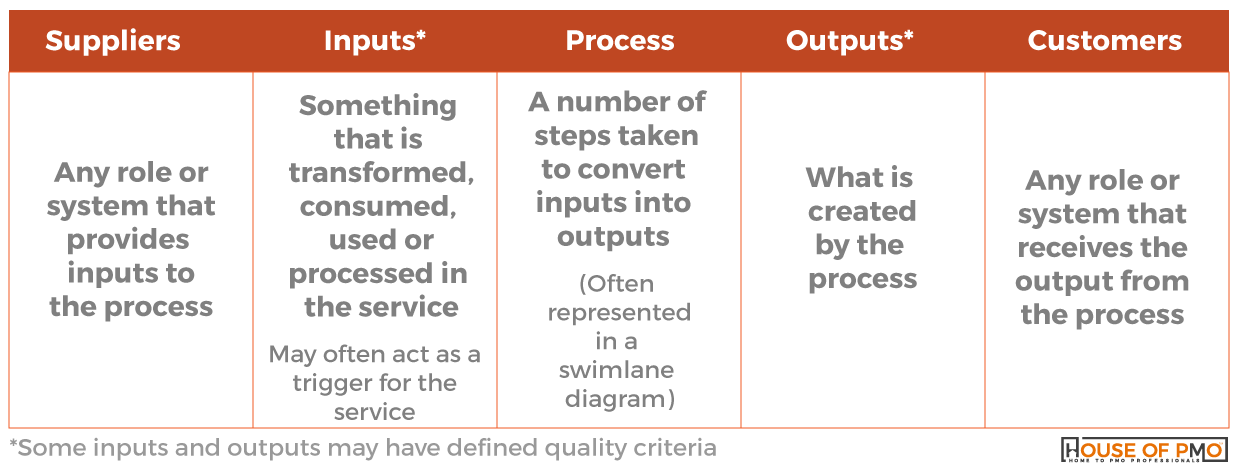
For some of the processes underpinning the service, the outputs of one process may by the input of another process. When designing the PMO service, these dependencies need to be considered.
The detailed procedures to be undertaken by the PMO(s) will also need to be defined and included in the relevant PMO Operations Handbooks. Procedures for monitoring the PMO services and any impact on PMO performance monitoring may also need to be designed or updated.
All Processes and procedures require testing prior to transitioning into PMO business as usual. This may include piloting the service with a selection of suppliers, customers and PMO Service Operatives.
Testing can be used to:
- confirm the governance and critical success factors are in place
- verify the process and procedures achieve the success criteria agreed with the customers
- confirm the resources are available to deliver the service to the required standard.
Undertaking the testing and pilot of a service also provides the opportunity to validate that the services will deliver the expected outcomes.
During the testing and pilot, the PMO service, processes and procedures (including the respective PMO Service Strategy, PMO Service Catalogue and PMO Handbook) may be modified in light of the results.
Following formal sign off of the service after testing/ pilot is completed (which may take several iterations), and an organisation readiness assessment, the PMO service (along with appropriate monitoring and control processes) can be transitioned into PMO business as usual, through a phased or big-bang approach. It is important to recognise that the successful implementation and embedding of many PMO services will require behavioural change by one or more individuals and therefore will need to be managed as organisational change to ensure the required behaviours are also embedded in order to deliver the desired outcomes. This may require one or more temporary supporting services to be implemented alongside the requested service.
5.2. Running a PMO Service
Delivery of the PMO Services can be seen as the ‘business as usual’ work of the PMO and, like other BAU activities requires ongoing management to ensure the required level of service is maintained and the objectives of delivering the PMO service are being achieved. This is supported by the monitoring of KPI reporting as detailed within the PMO Operations Handbook.
Risks and issues to the service will need to be managed, with appropriate escalation from PMO Service Operations, through PMO Delivery Management to PMO Service Ownership to agree and manage appropriate mitigation and action, which may include making changes to the PMO service or even closing the PMO service.
There are many other reasons why the PMO service may need to be changed. These include:
- Changes in the business context
- Feedback from customers, PMO Service Operatives or stakeholders
- Changes in policies or available tools and techniques
Some changes will be formally requested via a change request. Other changes will be undertaken through continuous improvement activities manged by the PMO Service Manager.
Any changes applied to the service require agreement with the PMO Service Owner. All changes need to be reflected in the PMO Service Strategy, PMO Service Catalogue and PMO Operations Handbook as appropriate.
5.3. Closing a PMO Service
There are many reasons why a PMO service requires closing. This can include:
- Reaching the date it was agreed to stop the PMO service (this is particularly relevant for temporary supporting services)
- Achieving the desired objective of the delivering the PMO service, which on being achieved, does not need the PMO service to continue to be delivered
- Resources required to deliver the PMO service are required for other work or are no longer available
- A request from the service stakeholders or PMO Service Owner to close the PMO service
- It is no longer more effective, efficient or economically advantageous for the PMO to deliver the service.
- It has been recognised that the level of service or desired outcomes cannot be achieved
- A new PMO service replaces or supersedes the current PMO service
- A change in focus for the PMO
Closing the service should be undertaken in an orderly fashion and with formal approval of the PMO Service Owner.
Similar to the implementation of the PMO service, closure of the service may require behavioural change by one or more individuals and the closure will need to be managed as an organisational change.
When closing the PMO service, all artefacts pertaining to the service should be reviewed to identify those that may be useful for future reference ie if the PMO reintroduces the PMO service, or another PMO in the organisation begins to deliver the service.
Downloads
Download the Addendum
Click here to download a copy of the full PMO Service Catalogue Addendum text.
Certification Services
Click here to download a lisk of services reference in the House of PMO Essentials courses.
